
Do you know your GBICs from your GPUs? Your DAS from your DIMMs? Moving into a career in IT can be like learning a new language. There are acronyms for almost everything, which can seem a little overwhelming if you’re starting out. Even if you’ve been working in IT for years, the continuous technological advancements, upgrades and new product releases can be a mind field! That’s why we’ve created a breakdown of the common acronyms you’ll come across to help give a better understanding of your devices and how they work.
Many of the below acronyms you may have heard of but might not be sure of their exact meaning. In this guide we list all of the acronyms you need to know when working with IT hardware.
Acronyms of some of our main products
.

CPU – Core Processing Unit
Also referred to as: Processor
Also referred to as a processor, the CPU is the primary component of a computer that processes instructions from hardware and software running on the computer.

DDR – Double Data Rate
Also referred to as: double pumped, dual-pumped, double transition
Double Data Rate is the advanced version of synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) which can transfer data twice as quickly, by transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. SDRAM sends signals once per clock cycle. DDR (double data rate) transfers data twice per clock cycle.

DIMM – Dual In-Line Memory Module
A module containing a circuit board comprising of a series of dynamic random access memory circuits, designed to be used in personal computers, workstations and servers.

ECC – Error Correction Code
Error correction code is used to verify data transmissions by locating and correcting errors, commonly used by random access memory (RAM) chips.
.
-min.png)
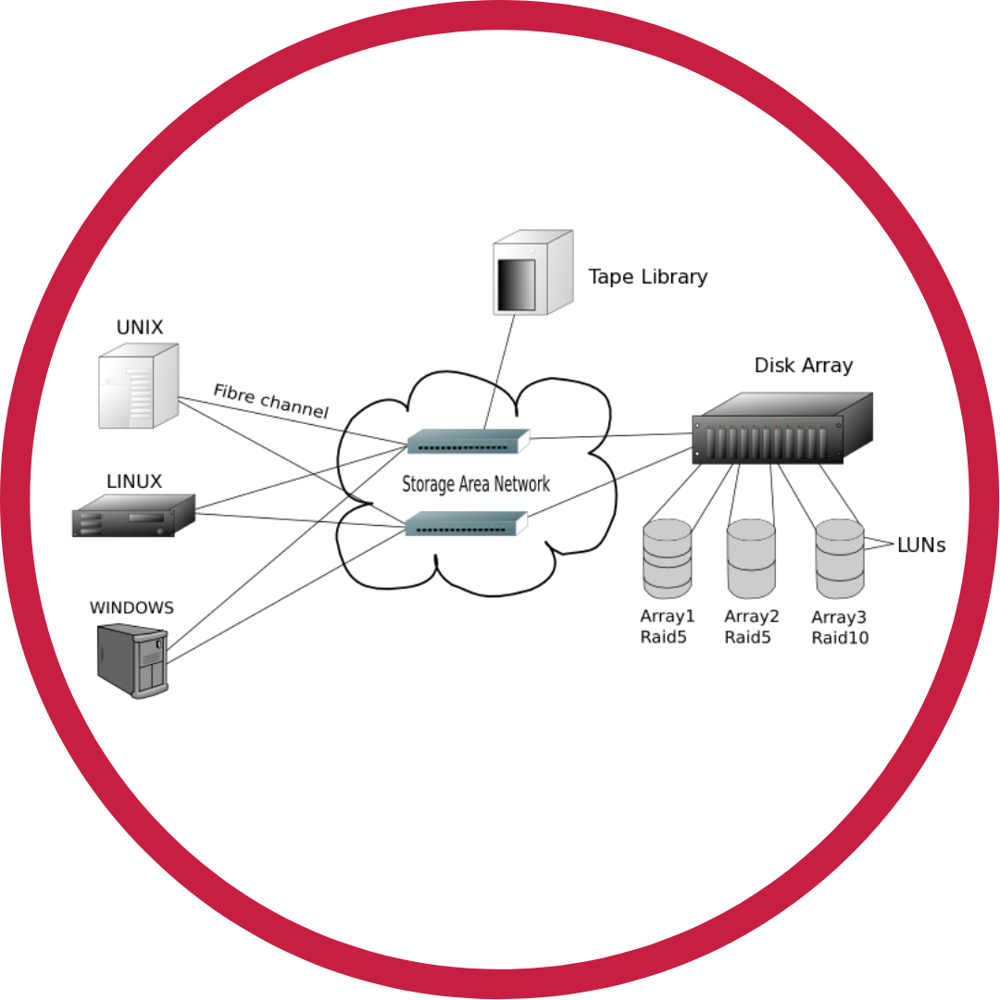
FC – Fibre Channel
A Fibre Channel is a high-speed data transfer protocol primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN).

GBIC – Gigabit Interface Converter
A transceiver that converts electrical optical signals to electrical currents and vice versa, typically used in Ethernet and fibre optic systems. It acts as an interface for high-speed networking, enabling network devices such as a router or switch to have support for different connections.

GPU – Graphics Processing Unit
A processor designed to manage and boost the performance of graphic operations, including 2D and 3D graphics.

HBA – Host Bus Adapter
Also referred to as: Host Controller, Host Adapter.
A Host Bus Adapter connects a computer, which acts as a host system, to other network and storage devices.

HDD – Hard Disk Drive
Also referred to as: Hard Drive
A Hard Disk Drive is a non-volatile data storage device, typically installed internally in a computer attached directly to the disk controller of the motherboard connected using an ATA, SCSI or SATA cable. A HDD is made up of spinning magnetized disks determining the speed your computer is able to access information.
.

iDRAC – Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller
Designed for secure local and remote server management, an Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller is used to help deploy, update and monitor servers.

ILO – Integrated Lights Out
A remote server management processor embedded on the system board of HP ProLiant and Blade Servers to allow remote controlling and monitoring of servers.

IP Phone – Internet Protocol Phone
IP Phone is a method of delivering voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the internet.

LRDIMM – Load Reduced Dual In-line Memory Module
A load-reduction dual in-line memory module (DIMM) used in servers containing a memory buffer (MB) chip that increases the speed of the memory, reduces the load on a server’s memory bus and reduces power consumption.

MSA – Modular Storage Array
A storage array, also called a disk array, is a data storage system for block-based storage, file-based storage, or object storage. Rather than store data on a server, storage arrays use multiple drives in a collection capable of storing a huge amount of data, managed by a central management system. Modular storage arrays are typically based on two controllers, which are kept apart from the unit’s disks. In essence, this ensures that, if one controller experiences a failure, the second will take over from the first automatically.
.
-min.png)
NIC – Network Interface Card
Also referred to as: Network Adapter and Ethernet Card
A Network Interface Card is a component that connects a computer to a computer network using an Ethernet cable.
-min.png)
NVME – Non-volatile Memory Express
A hardware interface for Solid State Drives (SSDs) designed to accelerate the transfer speed between enterprise and client systems using a computers Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) bus.

PSU – Power Supply Unit
Also referred to as: Power Supply, P/S and PS.
A power supply unit is a component that converts main AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of a computer.

RAID Controller – Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks
A RAID Controller is a system of data storage that uses multiple hard drives to store data. Various storage techniques can be used to achieve different levels of data redundancy, error recovery and performance improvement.

RAM – Random Access Memory
Also referred to as: primary memory, main memory and system memory.
RAM is a high-speed component that allows information to be stored and retrieved on a computer. It temporarily stores data which can be accessed randomly quickly, unlike a hard disk drive (HDD). RAM is volatile meaning it retains data as long as the computer is on, but is lost once it is turned off.
.

SAS – Serial Attached SCSI
A type of serial transmission protocol that moves data to and from computer storage devices such as hard disk drives and tape drives.
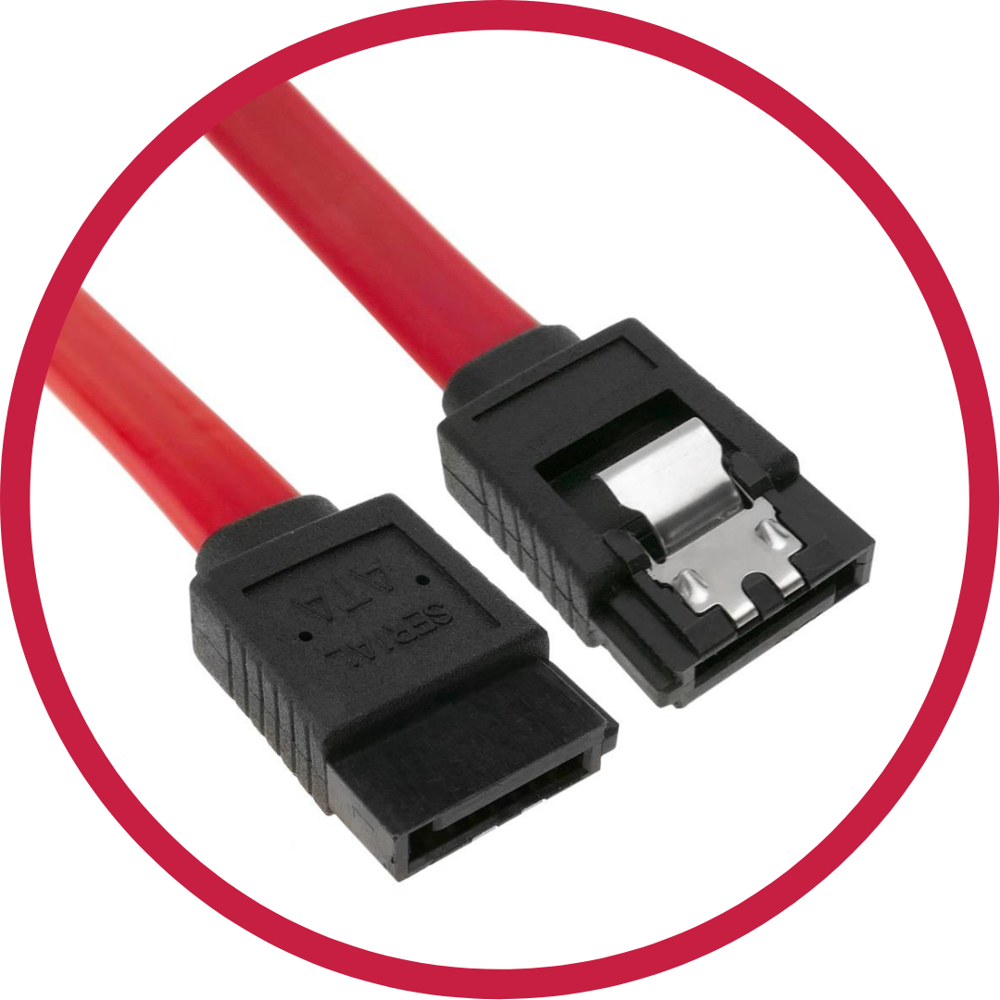

SATA – Serial Advanced Technology Attachment
Also referred to as: Serial ATA
A computer bus interface used to connect a host bus adapter to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives (SSD).
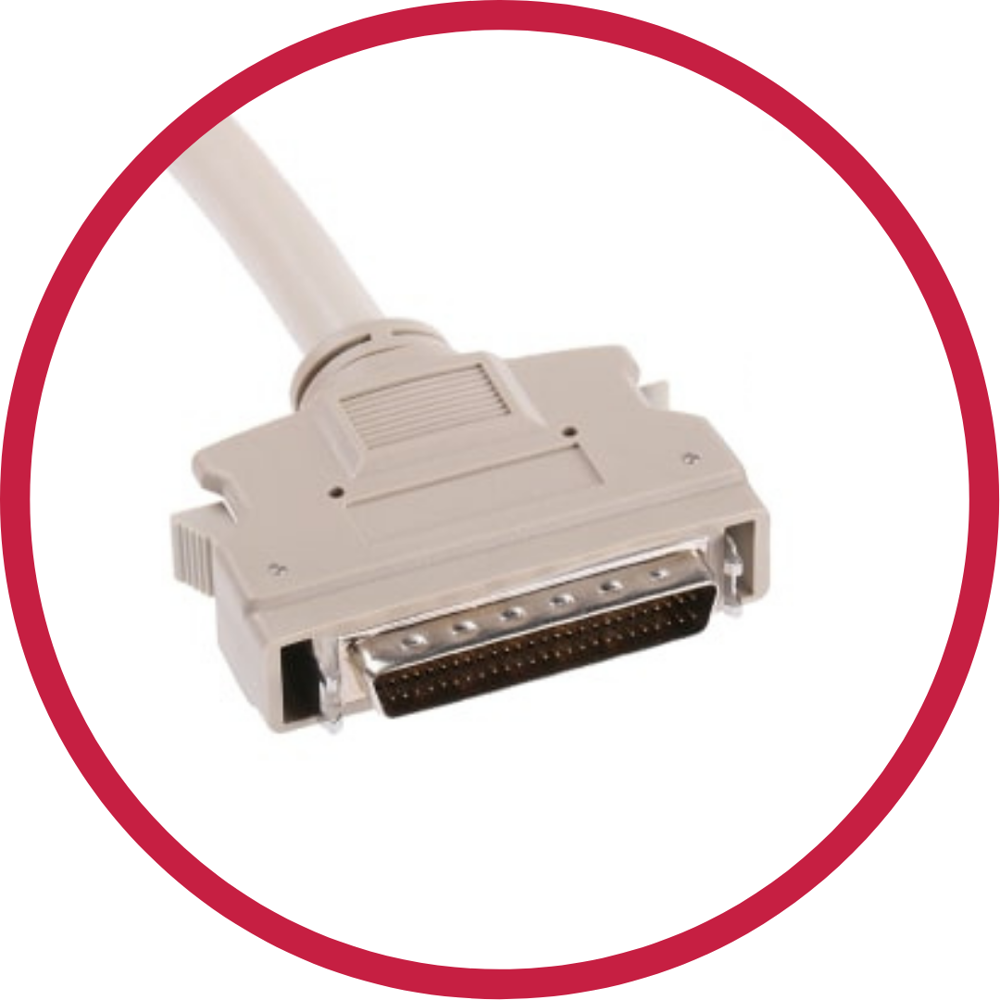

SCSI – Small Computer System Interface
An SCSI is a set of parallel interface standards used for connecting and transferring data from peripherals such as disk drives to computers.

SDRAM – Synchronised Dynamic Random Access Memory
SDRAM is Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) with an interface that is synchronous with the system carrying bus data, coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.
.

SFF – Small Form Factor / LFF – Large Form Factor
Hard Drive form factor relates to the size of the drive and determines the physical compatibility with the drive bays in a storage array, enclosure or server.
The most common form factor for enterprise class hard drives are large form factor and small form factor. SFF Hard Drives are 2.5inch long. LFF hard drives are 3.5 inches long.

SFP – Small Form-Factor Pluggable
Also referred to as: Transceiver
A device used to transmit and receive optical or electrical signals between network devices. They connect network cables to a variety of devices with media converters, network routers and switches.
SODIMM – Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module
SODIMM is a type of computer memory built using integrated circuits; a smaller alternative to a DIMM used in desktops and PCs.

SSD – Solid State Drive
A storage medium that uses non-volatile memory to hold and access data. Internal Solid State Drives connect to a computer using IDE or SATA connections. Unlike a hard disk drive (HDD) an SSD has no moving parts, allowing it to access data quicker and have a lower power consumption.
Intelligent Servers is a leading refurbished server, storage, networking and components reseller. We specialise in HP, Dell and Cisco, supplying thousands of businesses across Europe. Call: 01423 223430 Email: sales@intelligentservers.co.uk Live chat: Mon-Fri 9am-5.30pm



